Over the last several years we’ve seen a whole range of ideas regarding the architecture of systems. These include:
- Hexagonal Architecture (a.k.a. Ports and Adapters) by Alistair Cockburn and adopted by Steve Freeman, and Nat Pryce in their wonderful book Growing Object Oriented Software
- Onion Architecture by Jeffrey Palermo
- Screaming Architecture from a blog of mine last year
- DCI from James Coplien, and Trygve Reenskaug.
- BCE by Ivar Jacobson from his book Object Oriented Software Engineering: A Use-Case Driven Approach
Though these architectures all vary somewhat in their details, they are very similar. They all have the same objective, which is the separation of concerns. They all achieve this separation by dividing the software into layers. Each has at least one layer for business rules, and another for interfaces.
Each of these architectures produce systems that are:
- Independent of Frameworks. The architecture does not depend on the existence of some library of feature laden software. This allows you to use such frameworks as tools, rather than having to cram your system into their limited constraints.
- Testable. The business rules can be tested without the UI, Database, Web Server, or any other external element.
- Independent of UI. The UI can change easily, without changing the rest of the system. A Web UI could be replaced with a console UI, for example, without changing the business rules.
- Independent of Database. You can swap out Oracle or SQL Server, for Mongo, BigTable, CouchDB, or something else. Your business rules are not bound to the database.
- Independent of any external agency. In fact your business rules simply don’t know anything at all about the outside world.
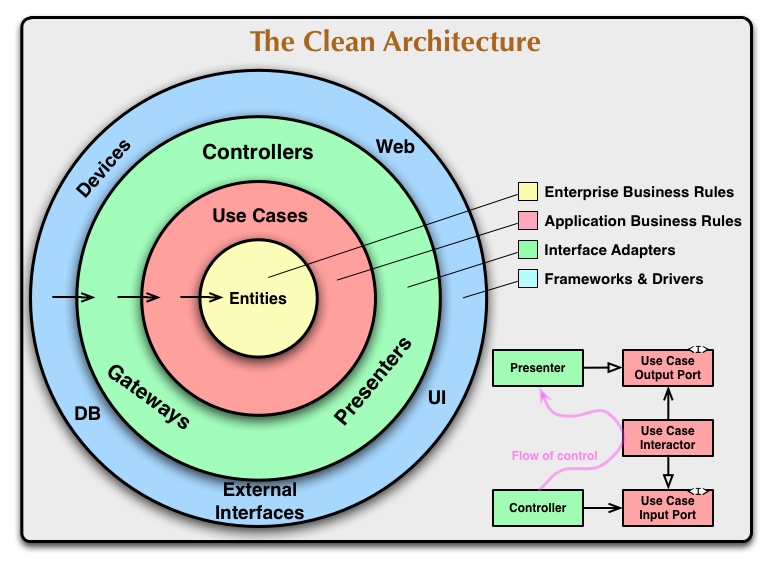
The diagram at the top of this article is an attempt at integrating all these architectures into a single actionable idea.
The Dependency Rule
The concentric circles represent different areas of software. In general, the further in you go, the higher level the software becomes. The outer circles are mechanisms. The inner circles are policies.
The overriding rule that makes this architecture work is The Dependency Rule. This rule says that source code dependencies can only point inwards. Nothing in an inner circle can know anything at all about something in an outer circle. In particular, the name of something declared in an outer circle must not be mentioned by the code in the an inner circle. That includes, functions, classes. variables, or any other named software entity.
By the same token, data formats used in an outer circle should not be used by an inner circle, especially if those formats are generate by a framework in an outer circle. We don’t want anything in an outer circle to impact the inner circles.
Entities
Entities encapsulate Enterprise wide business rules. An entity can be an object with methods, or it can be a set of data structures and functions. It doesn’t matter so long as the entities could be used by many different applications in the enterprise.
If you don’t have an enterprise, and are just writing a single application, then these entities are the business objects of the application. They encapsulate the most general and high-level rules. They are the least likely to change when something external changes. For example, you would not expect these objects to be affected by a change to page navigation, or security. No operational change to any particular application should affect the entity layer.
Use Cases
The software in this layer contains application specific business rules. It encapsulates and implements all of the use cases of the system. These use cases orchestrate the flow of data to and from the entities, and direct those entities to use their enterprise wide business rules to achieve the goals of the use case.
We do not expect changes in this layer to affect the entities. We also do not expect this layer to be affected by changes to externalities such as the database, the UI, or any of the common frameworks. This layer is isolated from such concerns.
We do, however, expect that changes to the operation of the application will affect the use-cases and therefore the software in this layer. If the details of a use-case change, then some code in this layer will certainly be affected.
Interface Adapters
The software in this layer is a set of adapters that convert data from the format most convenient for the use cases and entities, to the format most convenient for some external agency such as the Database or the Web. It is this layer, for example, that will wholly contain the MVC architecture of a GUI. The Presenters, Views, and Controllers all belong in here. The models are likely just data structures that are passed from the controllers to the use cases, and then back from the use cases to the presenters and views.
Similarly, data is converted, in this layer, from the form most convenient for entities and use cases, into the form most convenient for whatever persistence framework is being used. i.e. The Database. No code inward of this circle should know anything at all about the database. If the database is a SQL database, then all the SQL should be restricted to this layer, and in particular to the parts of this layer that have to do with the database.
Also in this layer is any other adapter necessary to convert data from some external form, such as an external service, to the internal form used by the use cases and entities.
Frameworks and Drivers.
The outermost layer is generally composed of frameworks and tools such as the Database, the Web Framework, etc. Generally you don’t write much code in this layer other than glue code that communicates to the next circle inwards.
This layer is where all the details go. The Web is a detail. The database is a detail. We keep these things on the outside where they can do little harm.
Only Four Circles?
No, the circles are schematic. You may find that you need more than just these four. There’s no rule that says you must always have just these four. However, The Dependency Rule always applies. Source code dependencies always point inwards. As you move inwards the level of abstraction increases. The outermost circle is low level concrete detail. As you move inwards the software grows more abstract, and encapsulates higher level policies. The inner most circle is the most general.
Crossing boundaries.
At the lower right of the diagram is an example of how we cross the circle boundaries. It shows the Controllers and Presenters communicating with the Use Cases in the next layer. Note the flow of control. It begins in the controller, moves through the use case, and then winds up executing in the presenter. Note also the source code dependencies. Each one of them points inwards towards the use cases.
We usually resolve this apparent contradiction by using the Dependency Inversion Principle. In a language like Java, for example, we would arrange interfaces and inheritance relationships such that the source code dependencies oppose the flow of control at just the right points across the boundary.
For example, consider that the use case needs to call the presenter. However, this call must not be direct because that would violate The Dependency Rule: No name in an outer circle can be mentioned by an inner circle. So we have the use case call an interface (Shown here as Use Case Output Port) in the inner circle, and have the presenter in the outer circle implement it.
The same technique is used to cross all the boundaries in the architectures. We take advantage of dynamic polymorphism to create source code dependencies that oppose the flow of control so that we can conform to The Dependency Rule no matter what direction the flow of control is going in.
What data crosses the boundaries.
Typically the data that crosses the boundaries is simple data structures. You can use basic structs or simple Data Transfer objects if you like. Or the data can simply be arguments in function calls. Or you can pack it into a hashmap, or construct it into an object. The important thing is that isolated, simple, data structures are passed across the boundaries. We don’t want to cheat and pass Entities or Database rows. We don’t want the data structures to have any kind of dependency that violates The Dependency Rule.
For example, many database frameworks return a convenient data format in response to a query. We might call this a RowStructure. We don’t want to pass that row structure inwards across a boundary. That would violate The Dependency Rule because it would force an inner circle to know something about an outer circle.
So when we pass data across a boundary, it is always in the form that is most convenient for the inner circle.
Conclusion
Conforming to these simple rules is not hard, and will save you a lot of headaches going forward. By separating the software into layers, and conforming to The Dependency Rule, you will create a system that is intrinsically testable, with all the benefits that implies. When any of the external parts of the system become obsolete, like the database, or the web framework, you can replace those obsolete elements with a minimum of fuss.
